How to check your WiFi GHz on iPhone? It’s easier than you think! Knowing whether you’re connected to the faster 5 GHz band or the more reliable 2.4 GHz band can significantly impact your internet speed and performance. This guide will walk you through finding this information on your iPhone, explaining the differences between the two frequencies and offering troubleshooting tips for slow WiFi.
We’ll cover everything from accessing your iPhone’s WiFi settings to interpreting the signal strength indicators. You’ll learn about the advantages and disadvantages of each frequency band, common causes of connectivity issues, and how to optimize your WiFi experience. Get ready to boost your iPhone’s internet performance!
Understanding WiFi Frequencies on Your iPhone: How To Check Your Wifi Ghz On Iphone
Your iPhone likely supports connecting to both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz Wi-Fi networks. Understanding the differences between these frequencies is crucial for optimizing your internet experience. This section explains the distinctions and helps you identify which frequency your iPhone is using.
Okay, so you want to know how to check your iPhone’s Wi-Fi GHz? It’s usually in your Wi-Fi settings. But hey, while you’re fiddling with settings, maybe you’re thinking about getting a DJI drone – check out this helpful guide on which DJI drone to buy to see which one’s right for you. Then, once you’ve decided, you can get back to figuring out that Wi-Fi GHz on your phone; it’s usually pretty straightforward once you know where to look!
2.4 GHz vs. 5 GHz WiFi Networks
Wi-Fi networks operate on different radio frequencies, primarily 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz. The 2.4 GHz band is older, more established, and offers better range and penetration through walls and other obstacles. However, it’s also more congested due to its widespread use by other devices like microwaves and Bluetooth. The 5 GHz band, while offering faster speeds and less congestion, typically has a shorter range and struggles to penetrate obstacles.
Advantages and Disadvantages of 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz
Choosing between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz depends on your priorities. Here’s a comparison:
| Feature | 2.4 GHz | 5 GHz |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Slower | Faster |
| Range | Longer | Shorter |
| Penetration | Better | Worse |
| Congestion | Higher | Lower |
Identifying Signal Strength of Each Band, How to check your wifi ghz on iphone
Unfortunately, iOS doesn’t directly display the signal strength for each band separately within the standard Wi-Fi settings. You can only see the overall signal strength of the currently connected network. To get a better understanding, you might need to use third-party network analysis apps (not covered here) or observe speed differences when moving closer or further from your router.
A strong signal doesn’t always guarantee high speed; other factors are involved.
Accessing WiFi Information on iPhone
Accessing your connected Wi-Fi network details on your iPhone is straightforward using the built-in iOS settings. This section guides you through the process.
To check your iPhone’s WiFi GHz, go to Settings > WiFi, tap the network name, and look for the “Frequency” option. Sometimes, though, troubleshooting network issues requires a quick check elsewhere; before diving deeper, you might want to see if is chat gpt down , as that could impact online services needed to access your router settings.
Once you’ve checked that, return to your iPhone’s WiFi settings to confirm the GHz.
Viewing Connected WiFi Network Details
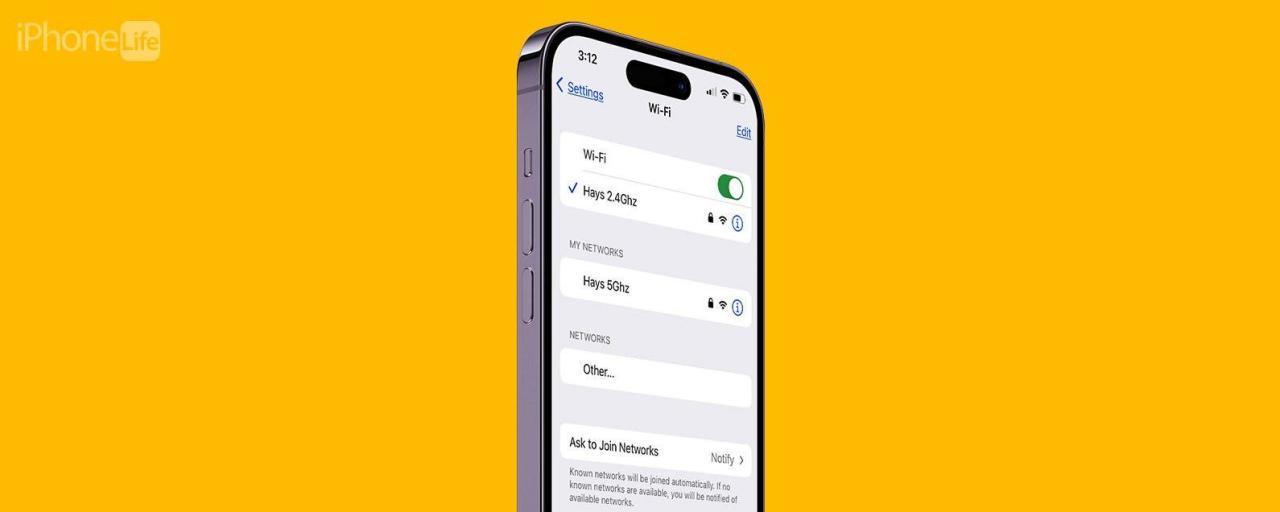
The standard path to view your connected Wi-Fi network details is through the iOS Settings app. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
- Open the Settings app (the grey icon with gears).
- Tap on Wi-Fi.
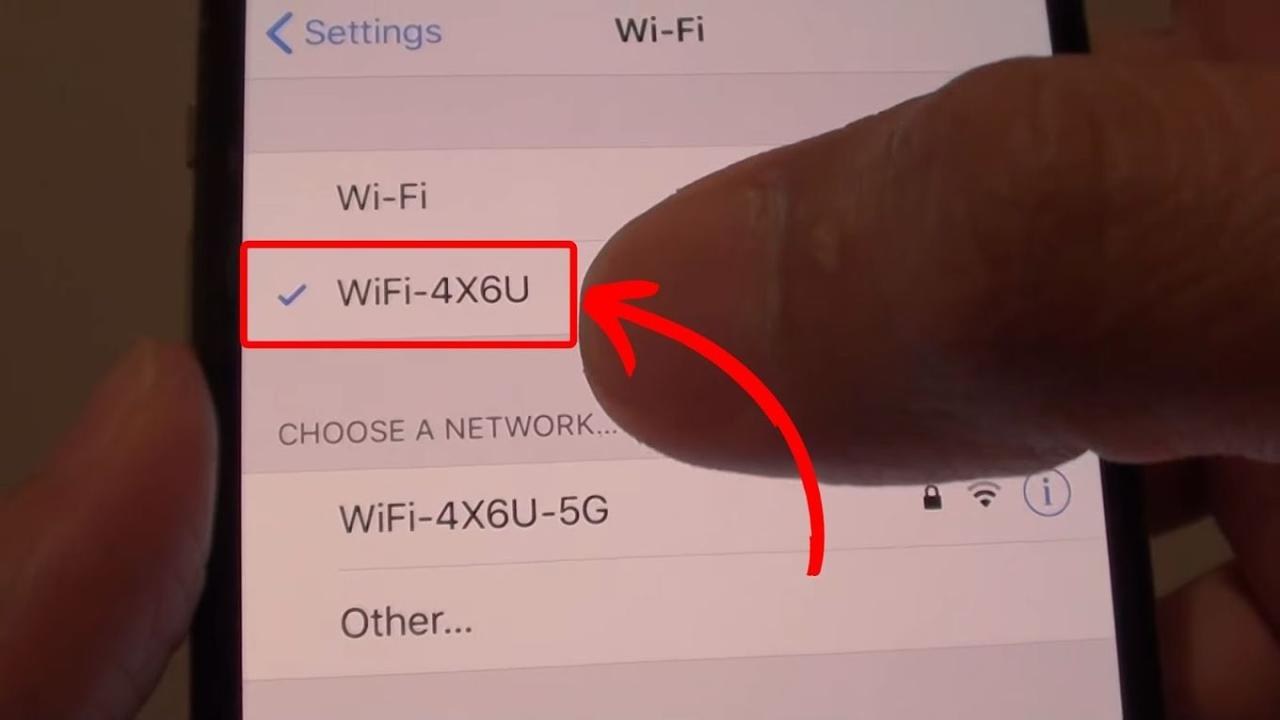
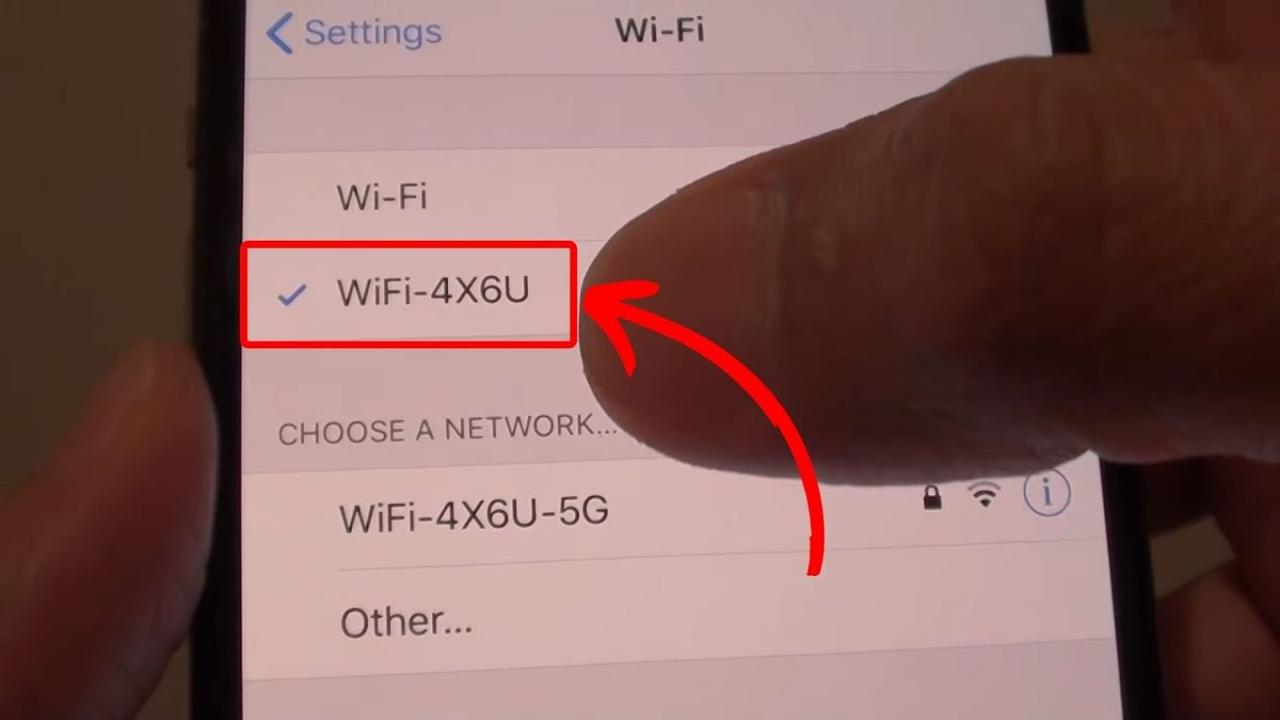
- Locate your currently connected Wi-Fi network. It will be listed at the top with a checkmark next to it.
- The network name (SSID) and signal strength (indicated by bars) will be displayed. Additional information might be available depending on your router’s configuration. A small “i” icon might be present to provide more detailed information.
Summary of WiFi Network Information Displayed in iOS Settings
The table below summarizes the information you typically find about your connected Wi-Fi network in iOS settings. Note that not all information is always displayed.
| Network Name | Signal Strength | Frequency | Security Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| ExampleNetworkName | (Signal strength bars, typically 1-4 bars) | (Not directly shown, often needs a third-party app) | WPA2 Personal, WPA3 Personal, etc. |
Interpreting WiFi Network Information
Understanding how the signal strength indicator translates to actual network performance and identifying factors influencing your Wi-Fi speed are essential for troubleshooting. This section addresses these aspects.
Signal Strength and Network Performance
The signal strength bars in iOS settings provide a relative indication of signal strength. Four bars generally suggest a strong signal, while one bar suggests a weak one. However, this isn’t a precise measure of speed. A strong signal might still result in slow speeds due to network congestion, router limitations, or interference.
Factors Affecting WiFi Signal Strength and Speed
Several factors can impact your Wi-Fi signal strength and speed, including:
- Distance from the router: The further you are, the weaker the signal.
- Interference: Other electronic devices (microwaves, cordless phones) can interfere with the Wi-Fi signal.
- Building materials: Walls, floors, and furniture can weaken the signal, especially for 5 GHz.
- Network congestion: Many devices using the same network can slow down speeds.
Range and Penetration Capabilities
2.4 GHz signals generally have a longer range and better penetration through obstacles compared to 5 GHz signals. 5 GHz signals, while offering faster speeds, are more susceptible to interference and signal degradation from walls and other obstructions.
Troubleshooting WiFi Connectivity Issues
Experiencing slow speeds or dropped connections? This section Artikels common causes and troubleshooting steps.
Common Causes of Slow WiFi Speeds or Connection Drops

Slow Wi-Fi or dropped connections can stem from various issues, including:
- Weak signal strength due to distance or interference.
- Network congestion from multiple devices.
- Router problems (hardware or software).
- Interference from other electronic devices.
- Incorrect network settings on your iPhone.
Troubleshooting Steps for WiFi Frequency-Related Issues
If you suspect your Wi-Fi frequency is contributing to connectivity problems, consider these steps:
- Try connecting to the other band (2.4 GHz or 5 GHz) if your router broadcasts both.
- Move closer to your router.
- Identify and remove potential sources of interference.
- Restart your router and iPhone.
Solutions for Weak Signals
- For weak 2.4 GHz signals: Consider a Wi-Fi extender or a mesh Wi-Fi system.
- For weak 5 GHz signals: Position your router strategically to minimize obstacles and interference. Consider a Wi-Fi extender specifically designed for 5 GHz.
Advanced WiFi Settings and Features
While iPhones don’t offer extensive manual control over Wi-Fi frequency selection, understanding your device’s capabilities and router configuration is helpful. This section covers relevant aspects.
Checking for 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz Support
Most modern iPhones support both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz Wi-Fi. You can check your router’s specifications to confirm whether it broadcasts on both frequencies. If it does, and your iPhone connects to only one, check the router’s settings to ensure both bands are enabled.
Connecting to Specific WiFi Networks Based on Frequency
If your router broadcasts separate SSIDs (network names) for 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz networks (e.g., “NetworkName_2.4” and “NetworkName_5”), you can manually select the network you prefer in your iPhone’s Wi-Fi settings.
Last Point
Mastering your iPhone’s WiFi settings is key to a smooth online experience. By understanding the differences between 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz networks and knowing how to check your connection details, you can troubleshoot problems quickly and enjoy faster, more reliable internet access. Remember to consider factors like distance from your router and potential interference for optimal performance. Happy browsing!
Key Questions Answered
Can I force my iPhone to connect to a specific WiFi frequency (2.4 GHz or 5 GHz)?
Not directly. Your iPhone will usually automatically select the best available frequency. However, if your router broadcasts separate SSIDs for each band, you can manually connect to the desired network.
Why is my 5 GHz WiFi connection slower than my 2.4 GHz connection?
Several factors can cause this. 5 GHz signals have less range and are more susceptible to interference from walls and other objects. Check your distance from the router and look for sources of interference.
So you wanna know how to check your iPhone’s Wi-Fi GHz? It’s usually buried in the settings, but hey, sometimes even tech stuff can feel like a mystery. While you’re figuring that out, you might want to check the open ai status if you’re using AI tools; a quick check there can save you frustration.
Once you’re back to your iPhone, remember to look for the Wi-Fi details in your network settings – you’ll find the GHz info there!
What does the signal strength (number of bars) actually mean?
Signal strength bars are a rough indicator of connection quality. More bars generally mean a stronger signal, but it doesn’t directly translate to speed. Other factors like network congestion also affect speed.
My WiFi keeps dropping. What should I do?
Try restarting your iPhone and router. Check for interference from other devices. Ensure your router’s firmware is up-to-date. Consider moving closer to the router or improving its placement.